Share Via
Table of Content
What is a network segmentation diagram?
A Network Segmentation Diagram visualizes how a computer network is divided into smaller parts or segments, each acting as an individual network. This process typically involves dividing the network based on VLANs by department or usage (like public and private), effectively isolating the group of connected devices within that network section.
The diagram provides a visual representation of different network segments, the connections between them, and the potential enforcement points such as firewalls or routers. It helps network administrators understand the architecture and layout, manage traffic effectively, and enhance security by understanding where and how data can move within the network.
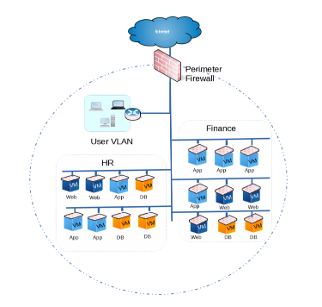
Example of a network diagram using traditional microsegmentation. Image credit: Deepsonline.com
Why is a network segmentation diagram important?
Network segmentation diagrams are essential for several reasons. Firstly, they enhance security by helping visualize different parts of the network, which helps limit access and unauthorized access. Additionally, these diagrams aid in regulatory compliance by demonstrating how sensitive data is protected and managed within the network. Understanding the structure and segmentation of a network is crucial for effective network management and troubleshooting.
How network segmentation diagrams can benefit organizations
Network segmentation diagrams provide numerous benefits to organizations. They help in enhancing security by isolating sensitive areas of the network, reducing the risk of cyber attacks spreading across the entire network.
By clearly defining and visualizing network segments, these diagrams facilitate better management and monitoring, leading to improved performance and reduced congestion. Additionally, they aid in compliance with regulatory standards by showcasing how data flows and is protected within the network. This level of organization and clarity ultimately supports more efficient and effective IT operations.
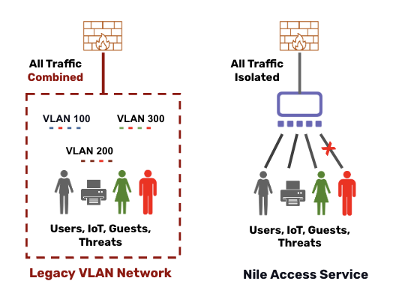
Nile Access Service simplified network segmentation diagram vs legacy diagram
Nile Access Service simplifies network segmentation and security by removing the need for VLANs and extensive network access control rules. Nile’s zero-trust solution isolates every device and their traffic from each other by redirecting it to a firewall or other enforcement system. Instead of using VLANs, Nile employs per-host tunnels to ensure that every user and device is placed in its own segment of one, preventing unauthorized access and lateral movement.
Making a network segmentation diagram
Creating a network segmentation diagram is a systematic process that ensures a clear and accurate representation of the network’s structure and security controls. This section will detail each step involved in this process.
1. Identify and map out all network components
Begin by identifying all the components in your network, including routers, access points, switches, firewalls, and servers. Documenting these elements helps in creating an accurate map of your network infrastructure. Use network discovery tools to automate this process and ensure no component is overlooked. This step is crucial for understanding the full scope of your network. Accurate mapping sets the foundation for effective segmentation.
2. Determine the logical segments or subnets
Next, identify the logical segments or subnets within your network. Consider factors such as department functions, IoT devices, security requirements, and traffic patterns when defining these segments. Logical segmentation helps isolate different parts of the network, enhancing security and performance. This process involves defining boundaries and access controls for each segment. Ensure that sensitive areas of the network are properly isolated to protect critical data.
3. Use diagramming tools to visually represent segments
Utilize diagramming tools to create a visual representation of the network segments. Tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, or online network diagramming software can be very effective. Start by laying out the network components and then draw the segments and connections between them. Clearly label each segment and component to avoid any confusion. This visual representation helps in understanding the network’s structure and aids in troubleshooting.
4. Illustrate connections and data flow paths
After defining the segments, illustrate the connections and data flow paths between them. Indicate how data travels from one segment to another, including any firewalls or security controls in place. This step is essential for understanding the interaction between different network parts. Highlight any critical paths where sensitive data might travel. This helps in identifying potential vulnerabilities and optimizing the network for better performance.
5. Review and update the diagram regularly
Finally, it is crucial to review and update the network segmentation diagram regularly. Networks are dynamic and constantly evolving, so the diagram must reflect any changes in infrastructure or security policies. Set a schedule for periodic reviews and updates. Engage with network administrators and security teams to ensure all changes are captured. Regular updates maintain the accuracy and relevance of the diagram, ensuring it remains a valuable tool for network management.
The Nile Access Service includes visualization tools that will help understand how a network is segmented. Its integrated tools like this ensure that changes in the current network architecture are automatically updated and reflected throughout the Nile Control Center application.
This automation simplifies the traditionally complex and manual process of defining and maintaining network segments, providing organizations with clear, real-time visibility into their network structure and enhancing overall security and performance.
What are the network segmentation diagram symbols?
Network segmentation diagrams use a variety of symbols to represent different components and functions within the network. These symbols provide a standardized way to depict complex network structures and ensure clarity in communication among IT professionals.
Router symbols
Routers are critical devices that direct traffic between different network segments. In diagrams, they are typically represented by a rectangular shape with arrows pointing in different directions. These arrows indicate the router’s capability to handle traffic to and from multiple segments. Proper representation of routers is essential for understanding data flow and network routing.
Switch symbols
Switches, which connect multiple devices within a network segment, are usually depicted as rectangles with several lines or dots indicating ports. These symbols show how devices within the same segment communicate with each other. Accurate depiction of switches helps in understanding the internal structure of each segment and its capacity.
Firewall symbols
Firewalls, which provide security by controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic, are often illustrated as brick walls or shields. These symbols highlight the security boundaries between different segments. Including firewall symbols in the diagram emphasizes the network’s security architecture and points where data is inspected and filtered.
Endpoint symbols
Endpoints, such as computers, servers, and other IoT devices today, are represented by various icons depending on their type. For example, a computer might be depicted by a desktop icon, while a server might be shown as a tower or rack. Clearly marking endpoints helps in identifying critical devices within each segment and their roles.
Connection and data flow symbols
Lines and arrows are used to represent connections and data flow between different network components. Solid lines typically indicate physical connections, while dashed lines might represent virtual or logical connections. Arrows show the direction of data flow, helping to visualize how information moves across the network. Using consistent symbols for connections and data flow ensures the diagram is easy to interpret.
What are the different layers of a network segmentation diagram?
Network segmentation diagrams are typically structured in layers, each representing a different aspect of the network’s architecture. Understanding these layers helps in comprehensively managing and securing the network.
Physical layer
The physical layer represents the hardware components of the network, including cables, switches, routers, access points and other physical devices. This layer is the foundation of the network and is crucial for understanding the physical connections and layout. Accurate representation of the physical layer ensures proper infrastructure management and helps in troubleshooting hardware-related issues.
Data link layer
The data link layer is responsible for node-to-node data transfer and error detection. It includes elements such as MAC addresses. This layer ensures that data is properly formatted for transmission and received correctly. Understanding the data link layer is essential for managing network traffic and ensuring reliable communication between devices.
Network layer
The network layer deals with routing and forwarding data packets across the network. It includes routers and IP addresses, defining how data moves from one segment to another. This layer is critical for ensuring efficient data flow and managing routing paths. Proper management of the network layer helps in optimizing performance and maintaining network integrity.
Transport layer
The transport layer ensures end-to-end communication and data transfer reliability. It involves protocols like TCP and UDP, which manage data flow control and error recovery. This layer is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring that information reaches its destination accurately. Understanding the transport layer helps in troubleshooting communication issues and optimizing data transfer.
Application layer
The application layer interacts with software applications to provide network services. It includes elements like web browsers, email clients, and other application-specific protocols. This layer is vital for supporting user interactions and ensuring seamless application performance. Managing the application layer involves ensuring that applications are correctly integrated with the network and perform efficiently.
What is the difference between the old and new model of network segmentation diagrams?
The evolution of network segmentation has led to significant differences between old and new models. Understanding these differences is crucial for leveraging modern network management practices and enhancing overall network security and performance.
In the old model of network segmentation, the focus was primarily on separating the internal network from the external network (the Internet), providing enhanced security and protection through firewalls and other perimeter security tools.
In this model, anyone or any device inside the network was automatically trusted, allowing for unrestricted movement within the network. The diagram of such a network would show clear demarcations between internal and external networks with security measures focused at the perimeter.
The new model of network segmentation, in line with the zero-trust network architecture, no longer assumes that internal devices or users can be fully trusted. It involves breaking down the internal network into smaller, isolated segments or zones.
Each of these segments can have its own set of access controls and security policies, and the trust is assigned based on verification of user/device identities, not their location within the network. In a diagram, the new model would show multiple internal segments, each with their own set of security controls, in addition to the perimeter security measures.
The main difference between the old and new models is therefore the shift from a binary trust model (internal trusted, external untrusted) to a more nuanced, context-dependent trust model (trust based on verified identities and context). This provides layered protection, enhanced security and minimizes the potential damage from internal threats or breaches.
Security and performance by default
The Nile Access Service is designed to provide organizations a zero trust network foundation by default. This facilitates a smooth transition to the new model of network segmentation, which relies on per device segmentation and isolation, dynamic access controls and more granular and flexible policy enforcement.
By incorporating automated monitoring and management tools, Nile ensures this automation reduces the need for manual configuration, thereby minimizing the risk of human error and enhancing operational efficiency. Ultimately, organizations can quickly adapt to new security threats and changing network demands, supporting a robust and resilient network infrastructure.
The Nile Access Service is the complete solution for enterprises looking to enhance network reliability, performance, and security.


