Share Via
Introduction
In this article, we explain how the Nile Access Service utilizes AI to make it possible for an enterprise network to be deployed with deterministic principles for design and installation. Result is a strong foundation for secure connectivity across your campus and branch locations, without surprises. If you would rather catch the demo before diving deeper, here it is in few minutes:
The Current Approach to Network Design
Enterprise network designers, aiming to maximize network performance, end up procuring hardware and software with various models. Selection of different product categories, individual SKUs and software licenses can usually be a daunting process.
Last time we checked, some of the enterprise networking vendors offer more than 300 options on their product catalogs – just to be able to set up wired and wireless connectivity in a building.
The process is daunting since it requires an understanding of how the myriad combinations of vendor’s hardware models, its licensing options, and software releases come together. A few pages of an ordering guide can help but does not bring back the hours you have to spend in order to understand the logic behind it all.
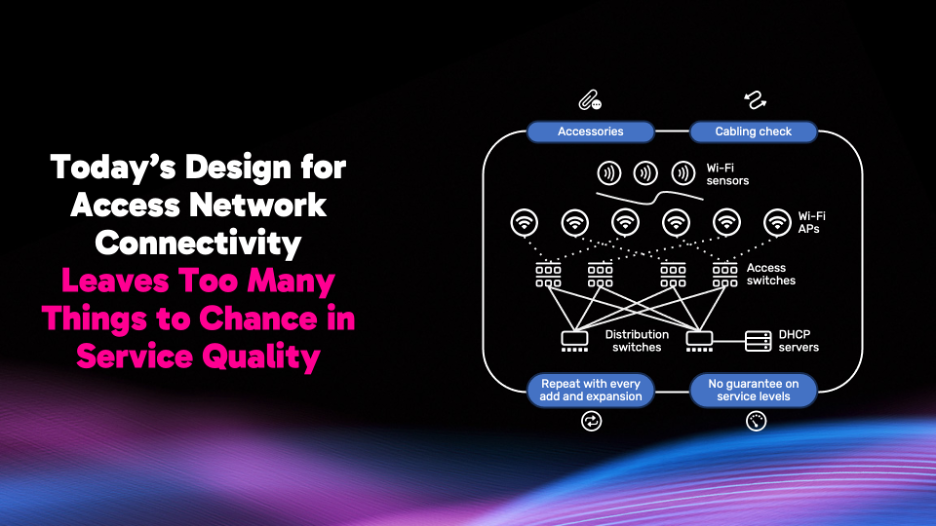
Fig 1. Today’s Network Engineering
At the end of it all, finalizing your combination often comes down to personal preference. Hence network design principles and actual implementation details can vary widely even within the same enterprise. Resulting “snowflake” networks within an organization make it impossible to guarantee any sort of performance expectations given the unpredictability behind the foundation that’s getting built. End users learn to live with the results on an ongoing basis by enduring unexpected performance issues in their favorite video conferencing application, or simply bad Wi-Fi coverage until the next refresh cycle.
Nile’s Modern Approach to Network Design
Nile standardizes the design and installation process for enterprise wired and wireless LANs with a deterministic approach for the Nile Service Blocks. By automating the design process from planning to deployment, this ensures that the network doesn’t deviate from one site to another, while guaranteeing network performance.
This is made possible by the Nile Access Service which is purpose built for cloud delivery and the Nile Services Cloud that includes AI networking and automation which is used to orchestrate and monitor the design process from the site survey to activation.
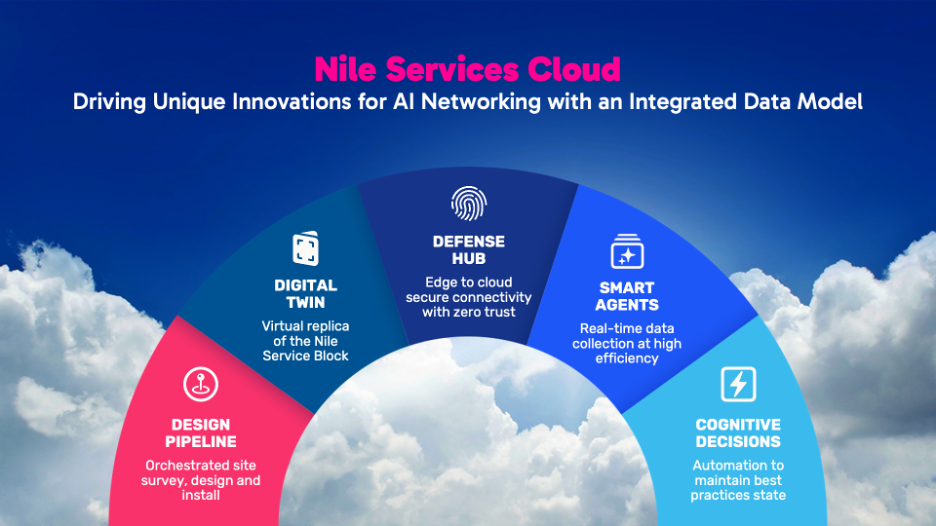
Fig 2. Nile Services Cloud
Automated Site Discovery & Site Survey
Design Pipeline helps orchestrate the site discovery and survey process. During the site discovery process, it helps the network design team gather the following.
- Site, building and floor data:
- # floors, # users, floor plan, ceiling type, walls & potential interferences
- Closet & Rack data
- Location of IDFs and MDFs
- Rack details that include, location, rack spacing, free rack unit slots and power availability
- Existing network equipment data
- Rack unit location for firewall, switches and patch panels
- Available free ports
During the wireless site survey process, it helps the design team gather the following:
- Users & devices data: # users, locations and access patterns, and
- Application data: commonly used applications, profile and traffic requirements
The site survey process generates a coverage map based on the location of APs and their coverage in the 2.4G/5G/6G bands to meet the desired user, device and application requirements.
An Automated BOM, Topology and Connectivity Plan
The Cognitive Decisions module in the Nile Services Cloud processes the site survey and site discovery data and automatically generates a Nile Planned Deployment (NPD), which includes a topology, Bill of Materials (BoM), and Connectivity Plan. The entire NPD bundle is accessible from Nile’s AI-enabled autopilot apps — Service Delivery Manager (SDM) and Customer Success Manager (CSM). This automatically generated deployment plan leads to the creation of a Digital Twin within the Nile Services Cloud.
The topology indicates how different network elements such as access points, switches and head-end are connected. The topology varies according to the size of the deployment. The network topology for the Nile Access Service also includes:
- A recommended Head-End type (virtual vs physical)
- Physical sensors and their location
- Connectivity between access points and switches based on salt-pepper redundancy requirements
A Bill of Materials includes the following:
- # distribution and access switches
- # access points
- # sensors
- # SFPs
- # AP mounting brackets
- Cable data: Cable type and required length
- Mounting tools, if any required
The Design Pipeline tracks the accuracy of the generated BOM through a “confidence meter” that compares the actual BOM against the auto generated BOM.
The difference between an actual and generated BOM is used to further auto-tune the BOM generation process. We continuously improve the accuracy of the BOM process to ensure that all the required materials are correctly identified and shipped to the customer location so that the installation proceeds without delays.
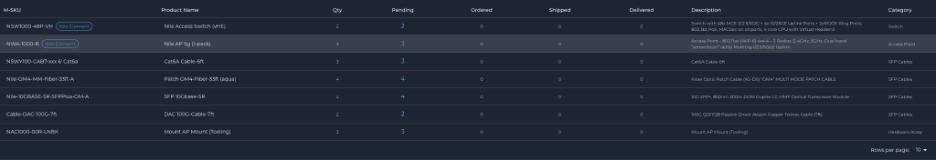
Fig 3. Bill of Materials (BOM) generated within the Nile AutoPilot application
Connectivity plan includes the following information:
- Closet Connectivity Plan
- # distribution and access switches
- # SFPs
- Cable data: Cable type and required length
- Source and destination connection details
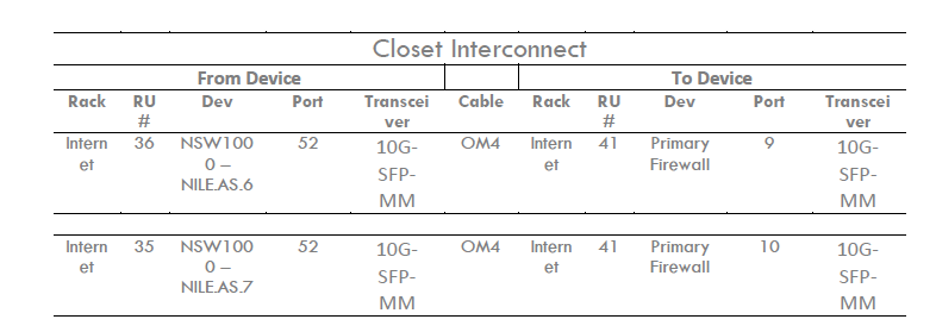
Fig 4. Closet Connectivity Plan
- Cabling Plan
- Floor plan
- Location of access points
- Destination MDF, rack name, rack unit and patch panel details
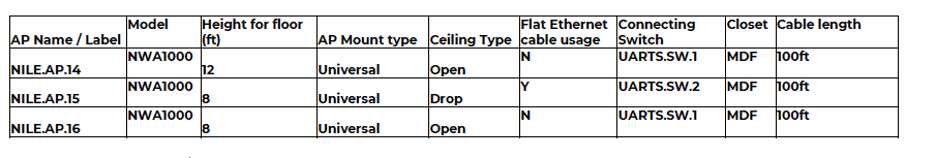
Fig 5. Cabling Plan
Installation
After completing the generation of a topology, bill of materials, and connectivity plan, Design Pipeline proceeds to automatically create work orders and assign it to installers.
The physical elements of a BOM are then shipped to the installation location. Design Pipeline makes the following information available to the installers via the Nile mobile app:
- Closet Connectivity Plan
- Cabling Plan
The mobile app guides the installers through the installation and activation of the various elements of Nile Planned Deployment (NPD).
After the installation is complete the Smart Agents spring to action and start streaming telemetry from the installed network elements to the Nile Services Cloud. Data within the Nile Services Cloud is then used to hydrate the Digital Twin and create a mapping between the digital version of the topology and the physical topology that was installed.
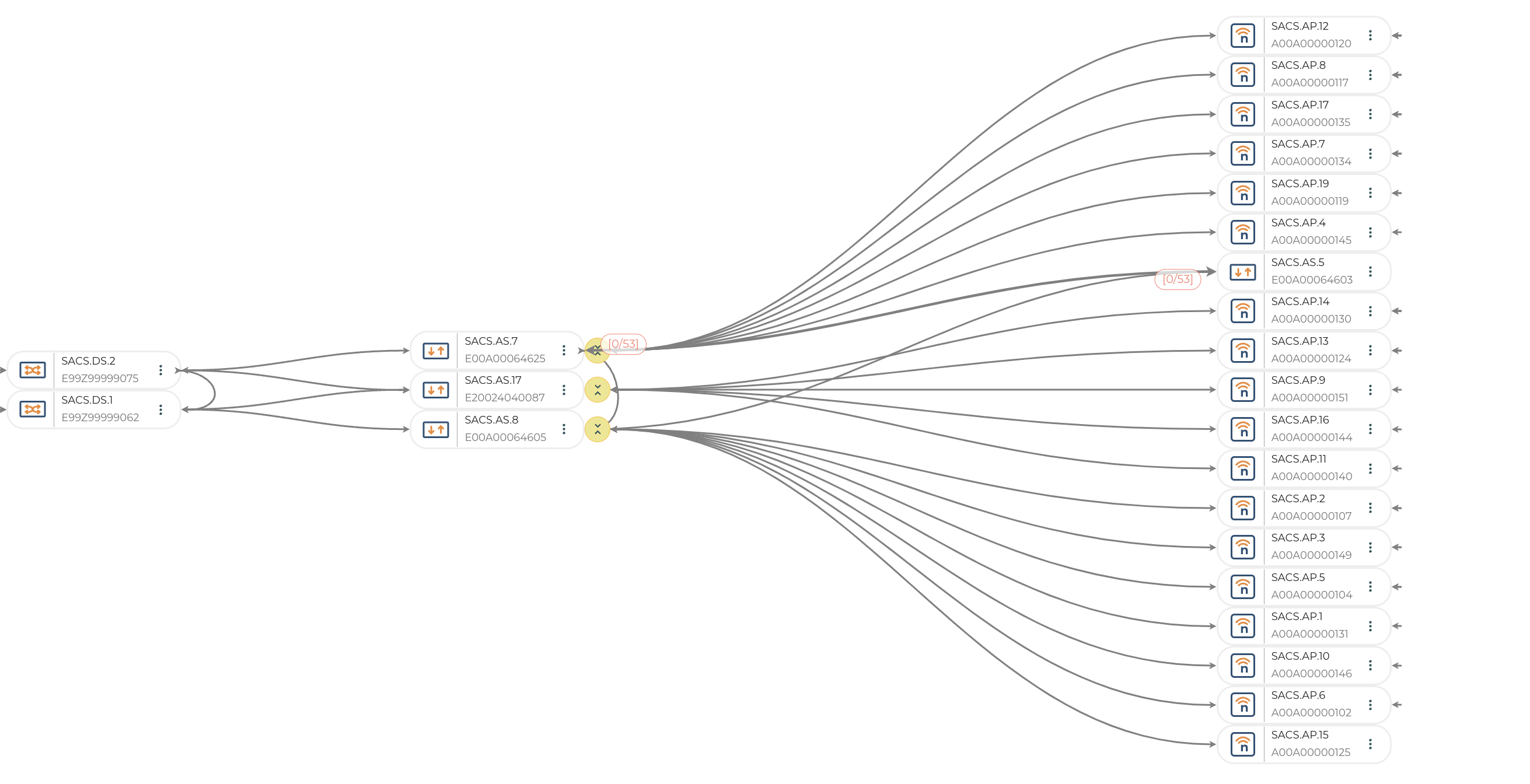
Fig 6. Digital Twin in the Nile Services Cloud
Deviation Detection
Nile Services Cloud’s Cognitive Decisions analyzes the streaming data from Smart Agents and looks for any deviations from the Nile Planned Deployment (NPD). Deviations may occur due to many reasons. Some of the reasons are given below:
- Installed cabling is not aligned with the Cabling Plan. Ex. APs are not connected in salt-pepper deployment i.e. to the right switches leading to non-redundant coverage
- Installed connectivity is not aligned with the Closet Connectivity Plan. Ex. switches may be connected with each other on wrong ports
- Sensors are not deployed at the location
- Redundant power supply is not connected with the switches
Cognitive Decisions captures these deviations and flags them immediately. If it detects any serious deviations such as incorrect connection during installation, it automatically blocks the installer from moving to the next installation step.
Post installation, if Cognitive Decisions encounters any deviations, it flags them and automatically creates a work order to address them.
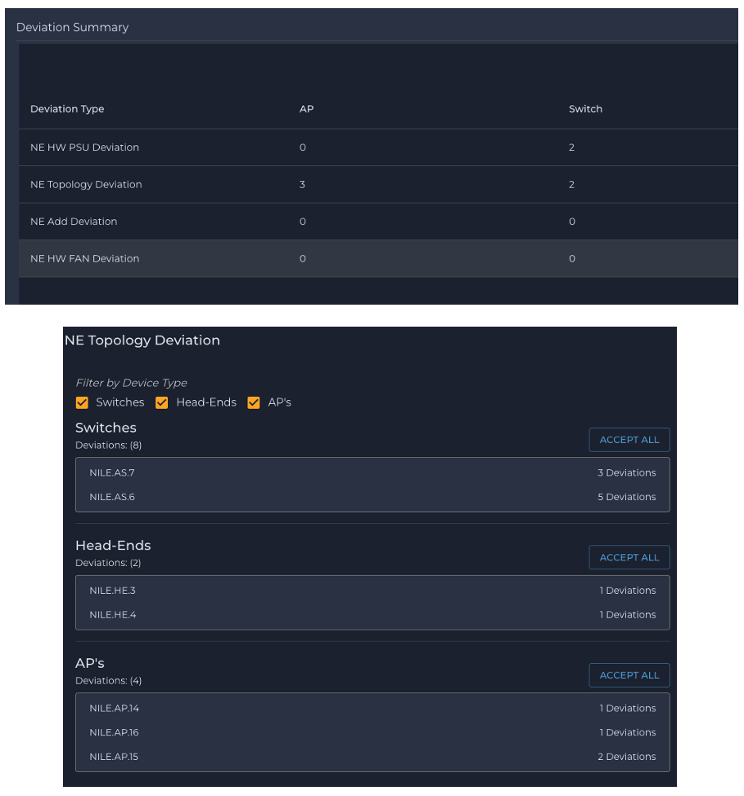
Fig 7. Deviations Tracked in the Nile AutoPilot application
The Digital Twin automatically selects the number of physical sensors required to monitor the network and their location. It also automatically selects the number of virtual sensors required to monitor the network and access points that host the virtual sensors.
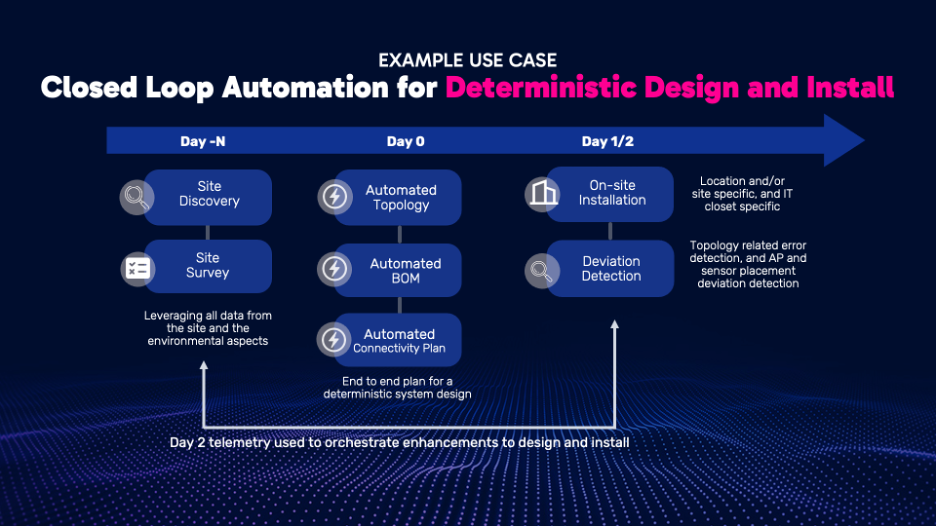
Fig 8. Enabling closed loop automation for deterministic install
Conclusion
Nile Services Cloud automates the network design process from site discovery to installation. It automatically generates the Nile Planned Deployment (NPD), Bill of Materials (BOM) and Connectivity plan and makes them available for installers through the Nile mobile application thanks to its Design Pipeline and other modules.
During installation and post installation the Nile Services Cloud continuously tracks the installed topology against the Nile Planned Deployment, flags any deviations and creates and tracks work orders to correct them, thereby ensuring the accuracy of installed topology.
This unique AI networking capability provides unheard of accuracy and speeds the deployment networks from weeks to days. No other networking vendor has this Day -1 capability, the data to build out a Digital Twin and extend Day -1 outcomes for resolving Day N issues that Nile can.