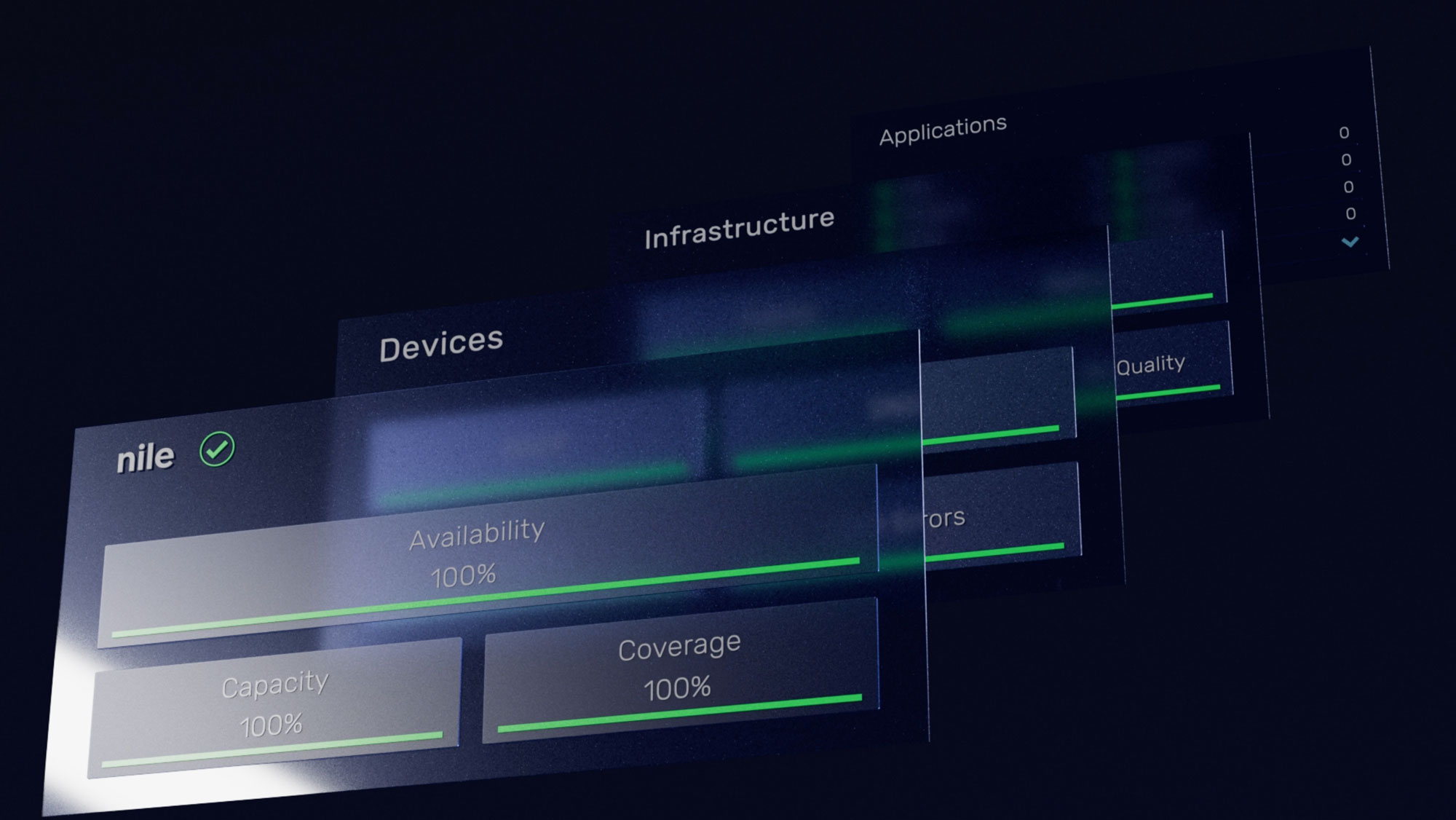
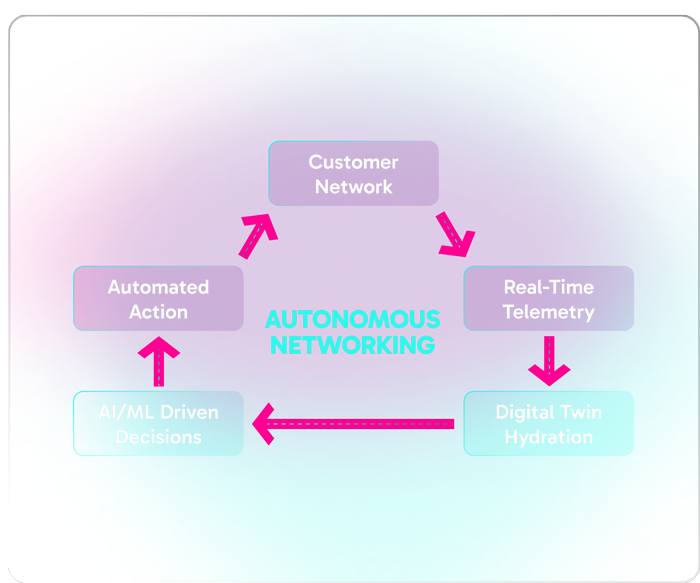
Autonomous Networking is a new paradigm that eliminates manual tasks and simplifies IT operations from Day -1 through Day N. Built on a vertically integrated, standardized as-a-Service model, the network infrastructure automatically deploys, self-configures, optimizes, and self-secures—eliminating the need for manual setup, troubleshooting, or ongoing management. By removing the complexities of traditional networking, it ensures performance, security, and scalability without constant IT oversight.
With these capabilities, IT teams are no longer burdened by maintenance and repair. Instead, they’re free to take on a more strategic role—enabling innovation and delivering greater value to the business.
Just as autonomous vehicles have redefined transportation by removing the need for a driver, autonomous networks represent a fundamental shift in how connectivity is delivered and managed—moving from hands-on control to intelligent, self-operating systems.
Today, most traditional vendors operate at a limited autonomy stage—where basic functions are automated, but IT teams still shoulder much of the manual oversight, configuration, and troubleshooting. These solutions may reduce some effort, but they stop short of delivering true operational freedom.
In contrast, Nile was built to provide a high level of autonomy from the start. Delivered as-a-Service and powered by AI, Nile networks self-deploy, self-tune, and continuously optimize—eliminating the need for routine human intervention. This shift unlocks dramatic improvements in efficiency, lowers operational costs, and strengthens security through continuous monitoring and automated response.